Table of content
Understanding DISC Communication Styles: Guide to Better Workplace Conversations
Learn how DISC communication styles can improve workplace conversations, enhance collaboration, and help you connect more effectively with any personality.
Understanding DISC communication styles is quickly becoming an essential skill for handling the modern workplace. Understanding different methods is essential in a workplace where good communication is the foundation of output, teamwork, and a peaceful atmosphere. This article will go in-depth on each of the DISC communication styles, their detailed mixes, and actionable ways for applying what you've learned.
What Are DISC Communication Styles?
DISC communication styles are part of the DISC model, which is a behavioral assessment tool that categorizes how people communicate based on four main personality types: Dominance, Influence, Steadiness, and Compliance. These are commonly referred to as the DISC 4 personality types, and each has a unique method of expressing ideas, responding to others, and managing interactions.
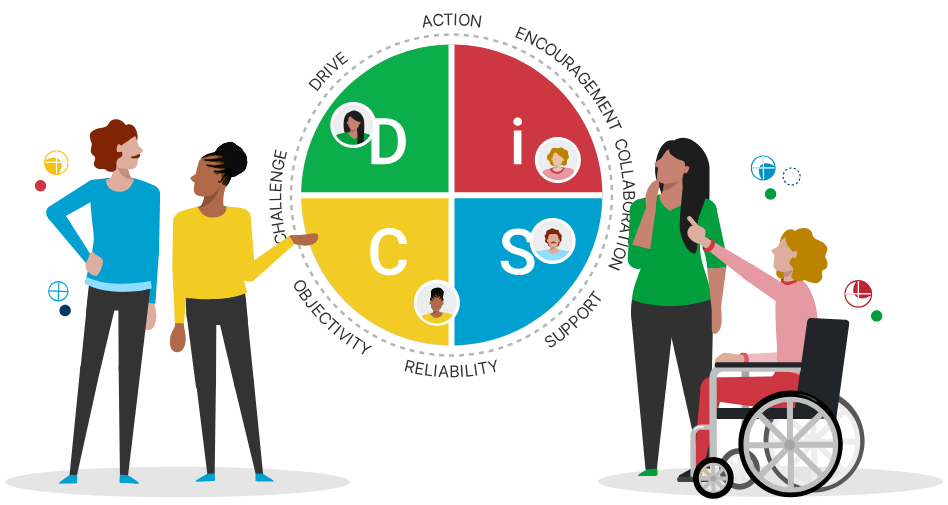
You might wonder: what are the 4 types of communication styles in DISC, and how do they show up in real-life situations? In basic terms, DISC communication styles explain how people prefer to communicate, whether they are more direct or reserved, fast-paced or cautious, and task-focused or people-oriented. Understanding these types allows people and teams to tailor their communication strategies to the preferences of others, resulting in more productive interactions and fewer conflicts. For example, a person with a Dominance (D) style may prefer short, results-driven conversations, while someone with a Steadiness (S) style values patience, harmony, and personal connection.
There are also expanded models, such as the 16 DISC personality types, which blend the core four to create more detailed assessments. These contribute to even deeper insights, particularly in complex workplace relationships.
4 DISC Communication Styles: An In-Depth Look
Understanding the core DISC model communication styles is critical for improving workplace interactions. While no one comes in precisely into a single box, recognizing these fundamental traits provides valuable insights.
Dominance (D) Style Communication
People with a high Dominance style are usually straightforward, goal-oriented, and decisive. They thrive on difficulties, excel at problem-solving, and are frequently seen as natural leaders who inspire action.
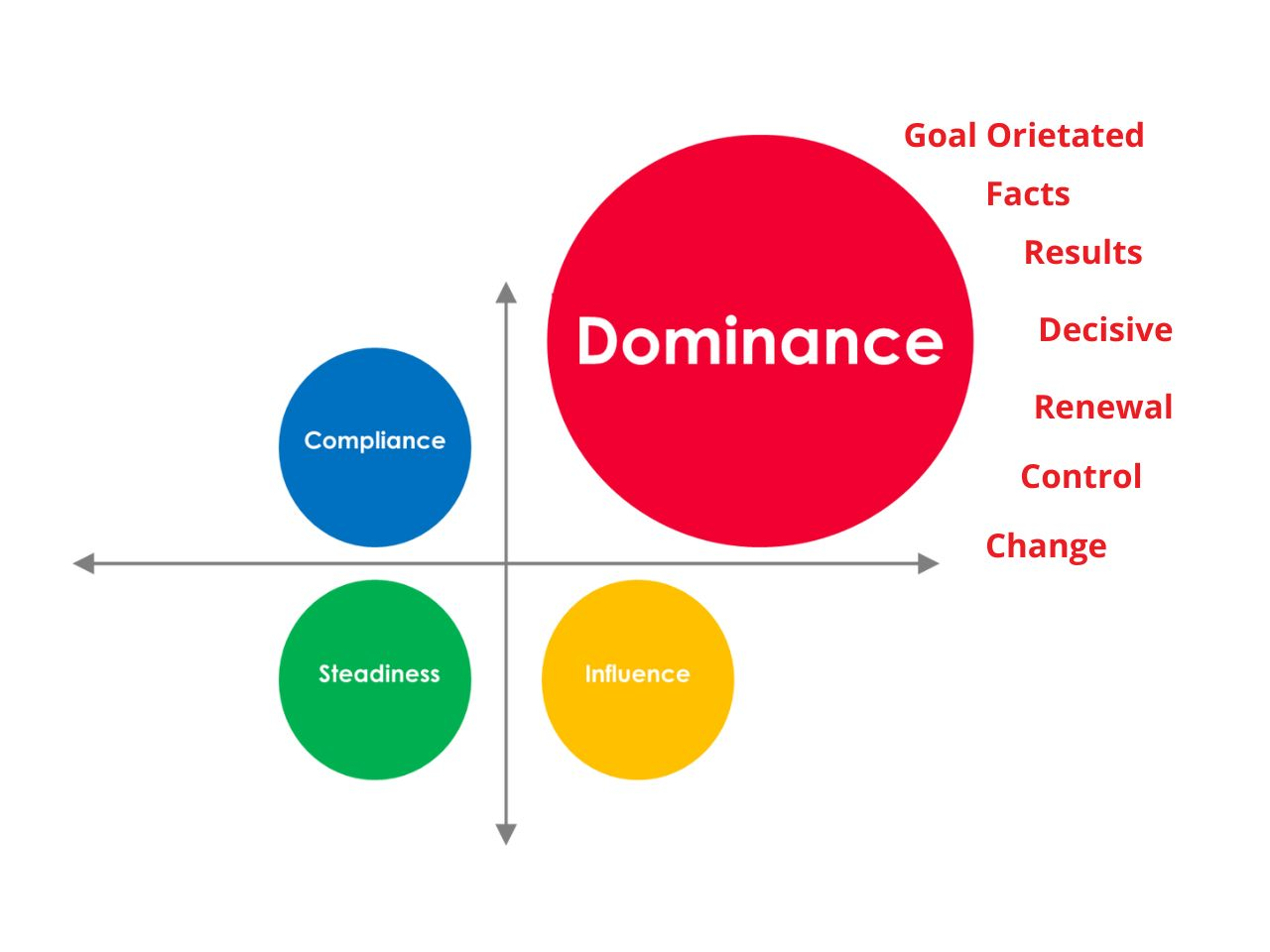
- Characteristics: Goal-oriented, confident, competitive, forceful, takes leadership, appreciates challenges, and achieves speedy results. They are frequently seen leading meetings, influencing decisions, and cutting through bureaucracy.
- Communication Preferences: Brief, to-the-point communication. They prefer efficiency and directness in responses, as well as strong action verbs and clear aims.
- Strengths: Excellent at pushing projects forward, making difficult decisions, quickly identifying and solving problems, and encouraging people to meet ambitious goals.
- Weaknesses: Can be regarded as extremely frank, impatient, demanding, or insensitive to others' feelings; may ignore details or refuse collaboration.
Tips for communicating with D-types:
- Be direct and concise.
- Focus on outcomes, not processes.
- Avoid unnecessary small conversations.
Influence (i) Style Communication
The influence style is characterized by optimism, enthusiasm, and sociability. These people are usually outspoken and persuasive, and they grow in settings where they can communicate with and motivate others.
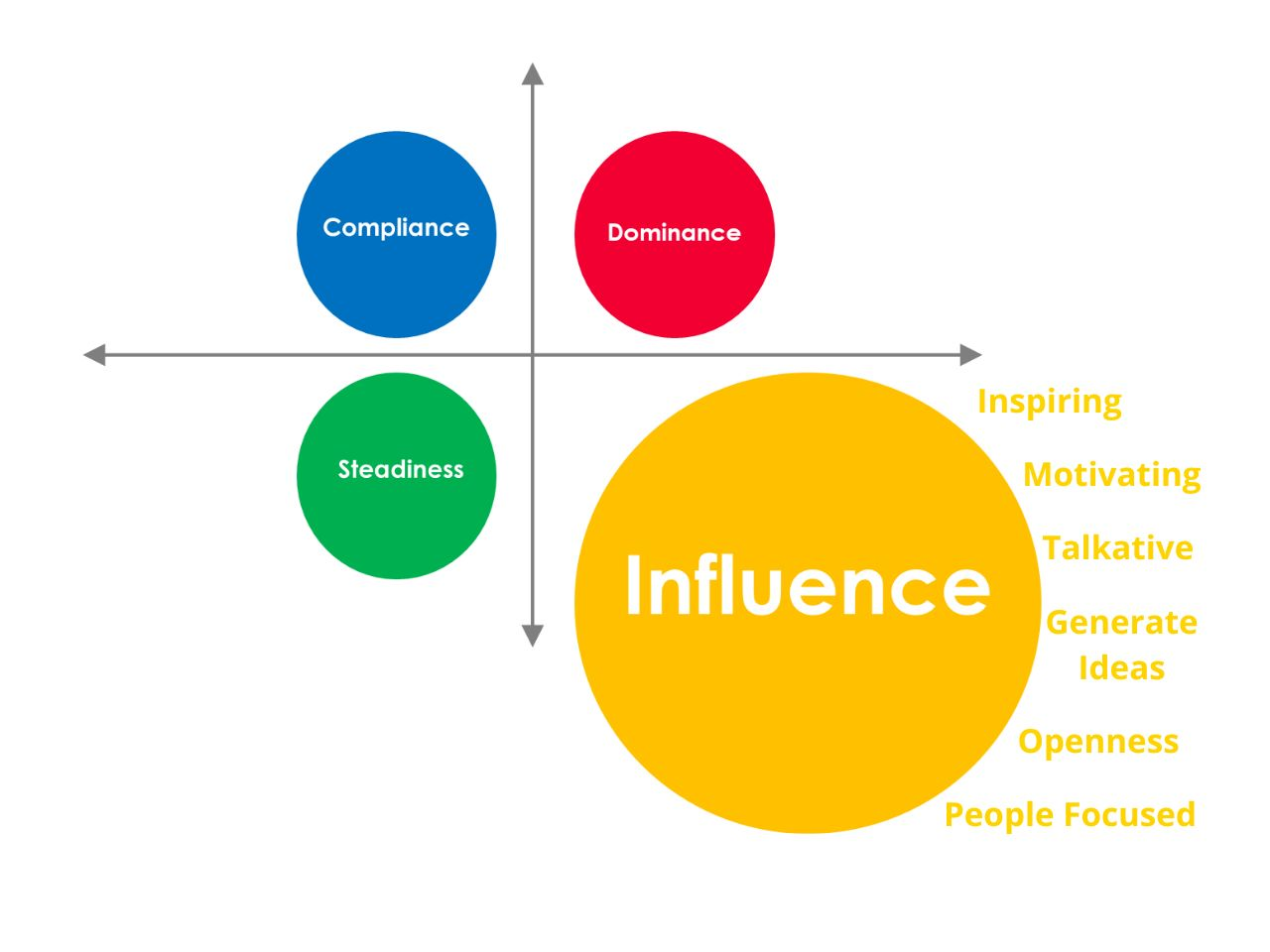
- Characteristics: Outgoing, charming, optimistic, collaborative, persuasive; enjoys networking and group activities. They are frequently the ones who establish connections, cheer on the team, and share exciting new ideas.
- Communication Preferences: Enjoys brainstorming, openly discussing ideas, and engaging in dynamic conversations. Positive feedback and recognition are important to them, and they like engaging and inspirational communication.
- Strengths: Motivates and inspires people, fosters great team relationships, and succeeds in sales, public relations, and presentations. They excel in fostering positive team dynamics and creative thinking.
- Weaknesses: Can be unorganized, impulsive, or prone to over-promising; difficulties with paying close attention to detail or avoiding painful realities in favor of harmony.
Tips for communicating with i-types:
- Exhibit energy and positivity
- Make space for personal interaction.
- Avoid being overly strict or detail-oriented.
Steadiness (S) Style Communication
People with a high Steadiness style are noted for their patience, dependability, and cooperative nature. They cherish harmony and security and desire a consistent, predictable work atmosphere.
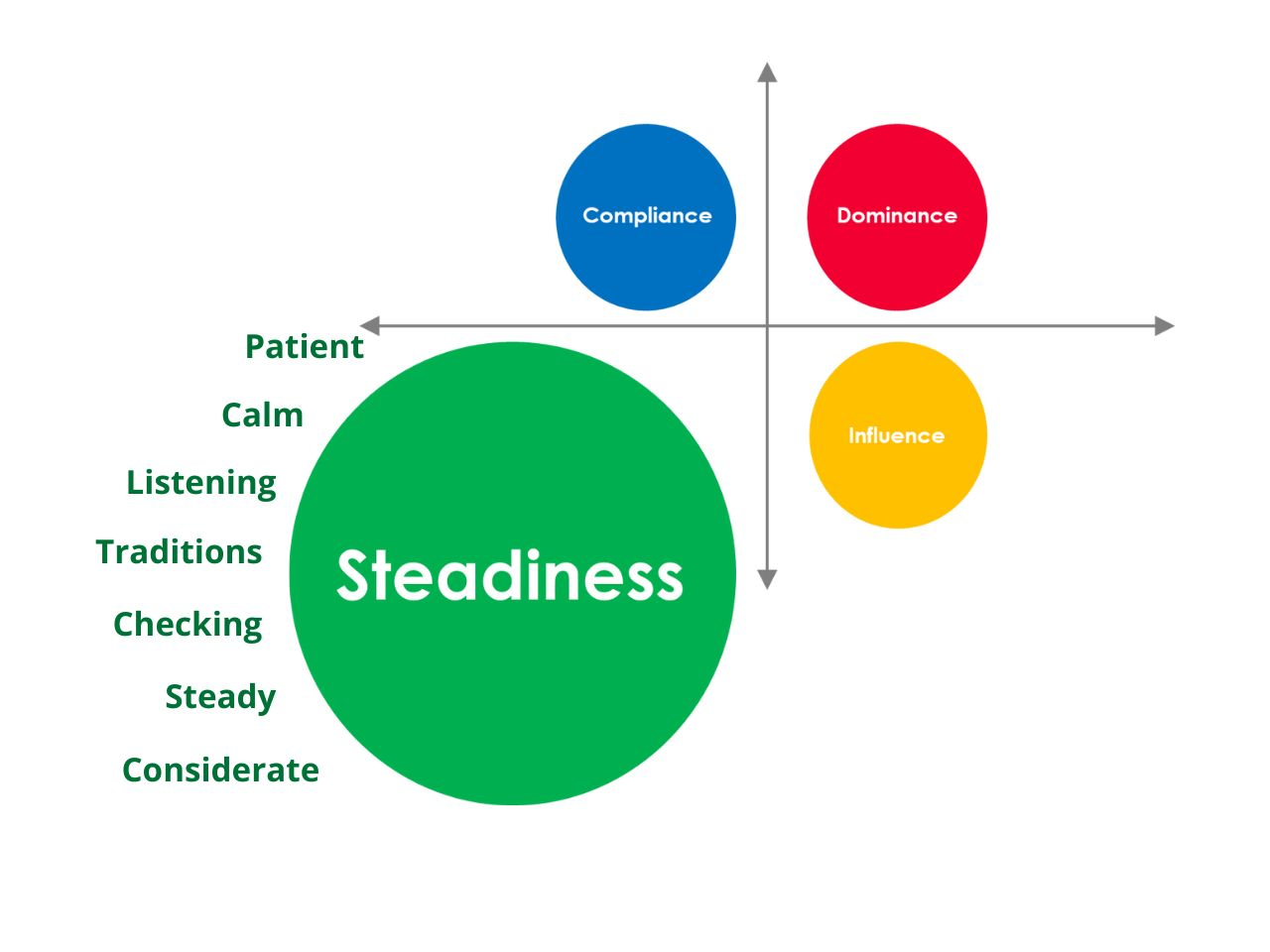
- Characteristics: Calm, dependable, supportive, good listener, team player, consistent, loyal, and enjoys predictable routines. They are frequently the backbone of a team, maintaining stability and offering a consistent presence.
- Communication Preferences: Respects the truth and likes straightforward, consistent, and well-structured communication. They are great listeners who love detailed explanations.
- Strengths: Excellent at establishing long-term relationships, giving steady assistance, promoting team stability, and completing assignments on time. They are exceptionally patient coaches and mentors.
- Weaknesses: Can be hesitant to fast change, hesitant when presented with uncertainty, or vulnerable to avoiding essential conflict to maintain peace; tends to absorb stress.
Tips for communicating with S-types:
- Be kind and sincere
- Give them time to respond
- Avoid rushing or pressuring them
Compliance (C) Style Communication
The Compliance style emphasizes quality, precision, and rationality. These individuals are analytical and exact and follow rigorous standards and established procedures.
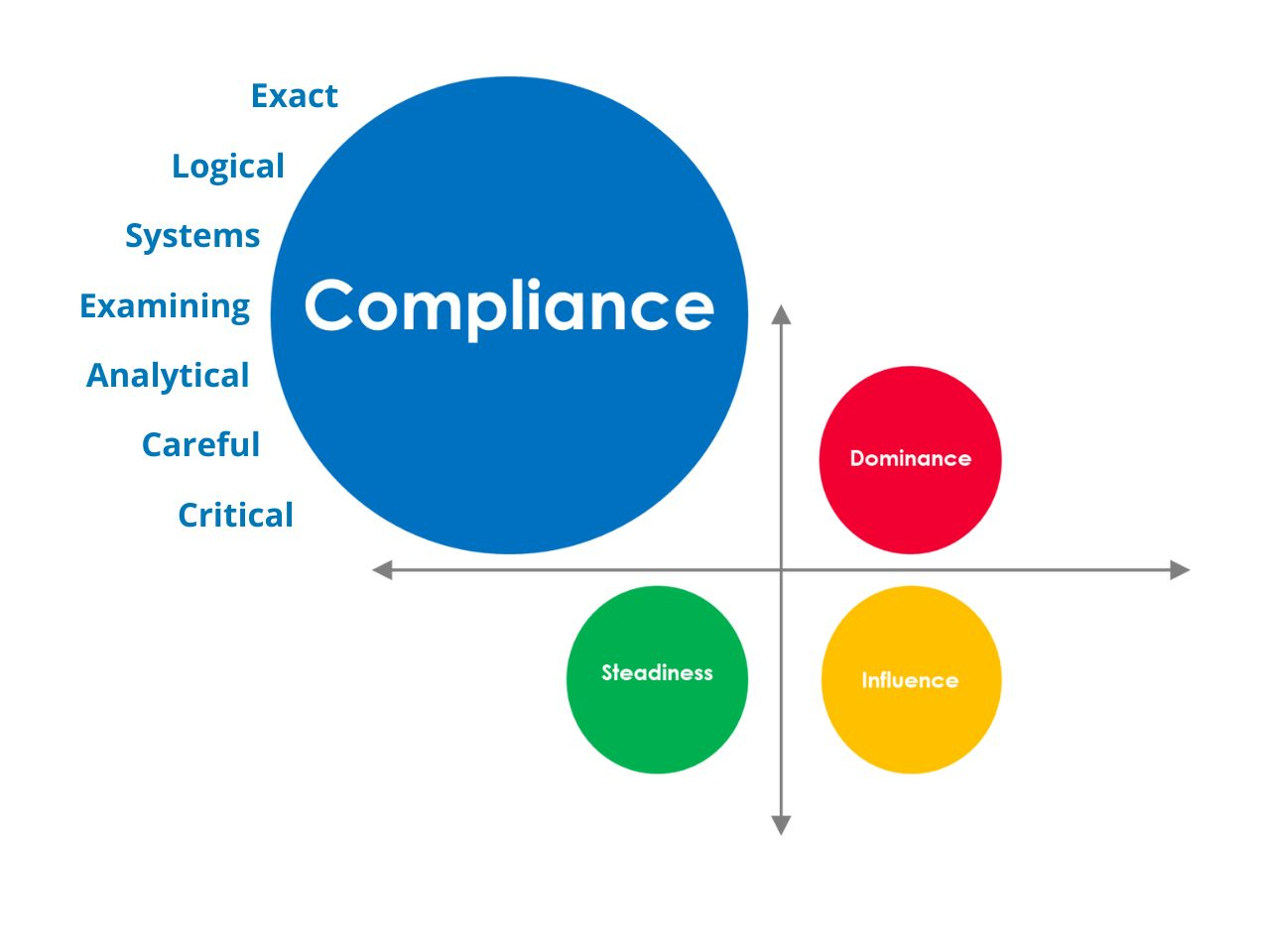
- Characteristics: Analytical, detail-oriented, careful, and courteous, with an emphasis on correctness, experience, and precision. They are frequently responsible for quality control, thorough data analysis, and protocol following.
- Communication Preferences: Requires detailed knowledge, facts, data, and logical reasoning. They prefer textual communication for clarity and accuracy and may be reserved in group conversations.
- Strengths: Delivers high-quality, accurate, and thorough work, excels at problem-solving, critical analysis, and ensuring standard and regulatory compliance. They thrive in identifying hazards and improving procedures.
- Weaknesses: Can be too critical, prone to perfectionism, resulting in delays, or struggle with uncertainty and making quick choices without enough facts.
Tips for communicating with C-types:
- Be well-prepared and thorough
- Stick to facts over feelings
- Avoid vague or emotional appeals
Other DISC Communication Styles: The 8 Style Blends
Although the DISC model is based on four main communication styles, most people do not fit neatly into any of them. In real life, individuals frequently exhibit a combination of two nearby types, giving 8 DISC communication style combinations. These blends provide a more comprehensive and realistic understanding of how people express themselves.
1. DC (Dominance + Compliance)

- Characteristics: Task-oriented, focused, and analytical. Like high-D people, DC types are goal-oriented, but they also be mindful of rules, processes, and accuracy.
- Communication Preferences: Expect direct, fact-based conversations. They prefer structure and efficiency, and may be skeptical without supporting evidence.
- Communication tip: Be concise but prepared to provide details and logic to back up your points.
2. CD (Compliance + Dominance)

- Characteristics: Independent thinkers with high standards. CD types prioritize accuracy and objectivity while showing a results-driven mindset.
- Communication Preferences: Formal, controlled, and critical when necessary. They often challenge ideas that lack data.
- Communication tip: Respect their need for structure; be well-prepared and show how your ideas align with their standards.
3. Di (Dominance + Influence)

- Characteristics: Bold, fast-paced, and people-oriented. Di types are natural leaders who like action and visibility.
- Communication Preferences: Persuasive and energetic with a strong desire to win others over while pushing for results.
- Communication tip: Match their energy, stay on topic, and highlight both people benefits and goals.
4. iD (Influence + Dominance)
- Characteristics: Expressive and confident, with a flair for motivating others. iD types are optimistic but not afraid to take charge.
- Communication Preferences: Loud, passionate, and sometimes impulsive. They love big ideas and quick decisions.
- Communication tip: Be open to brainstorming and let them lead discussions—just help keep them focused.
5. iS (Influence + Steadiness)
- Characteristics: Friendly, accommodating, and warm-hearted. iS types thrive on connection and harmony.
- Communication Preferences: Positive and supportive with an emphasis on group morale and collaboration.
- Communication tip: Use a warm, inclusive tone; avoid confrontation and be genuinely interested in their opinions.
6. Si (Steadiness + Influence)

- Characteristics: Relationship-focused and cooperative. Si types value team bonding and a smooth process.
- Communication Preferences: Calm, friendly, and encouraging. They may avoid tension and prefer slow, steady dialogue.
- Communication tip: Be patient, listen actively, and take time to build trust.
7. SC (Steadiness + Compliance)
- Characteristics: Dependable and systematic. SC types prefer stability and dislike sudden change. They like clear procedures and thoughtful communication.
- Communication Preferences: Measured and careful. They tend to listen more than speak and choose words with intention.
- Communication tip: Offer reassurance, use a steady tone, and give them time to process information.
8. CS (Compliance + Steadiness)
- Characteristics: Cautious, supportive, and private. CS types value correctness and often work behind the scenes.
- Communication Preferences: Formal, respectful, and detail-oriented. They dislike pressure or the spotlight.
- Communication tip: Provide clear expectations, maintain a calm tone, and avoid surprises.
Applying DISC for Improved Communication
Understanding the DISC model communication styles is just the beginning. The true value comes when you start applying those ideas to your daily interactions. Whether you're working or resolving conflict, adapting to varied communication styles is an effective skill. Throughout this section, we'll provide practical DISC communication styles examples to illustrate effective application.
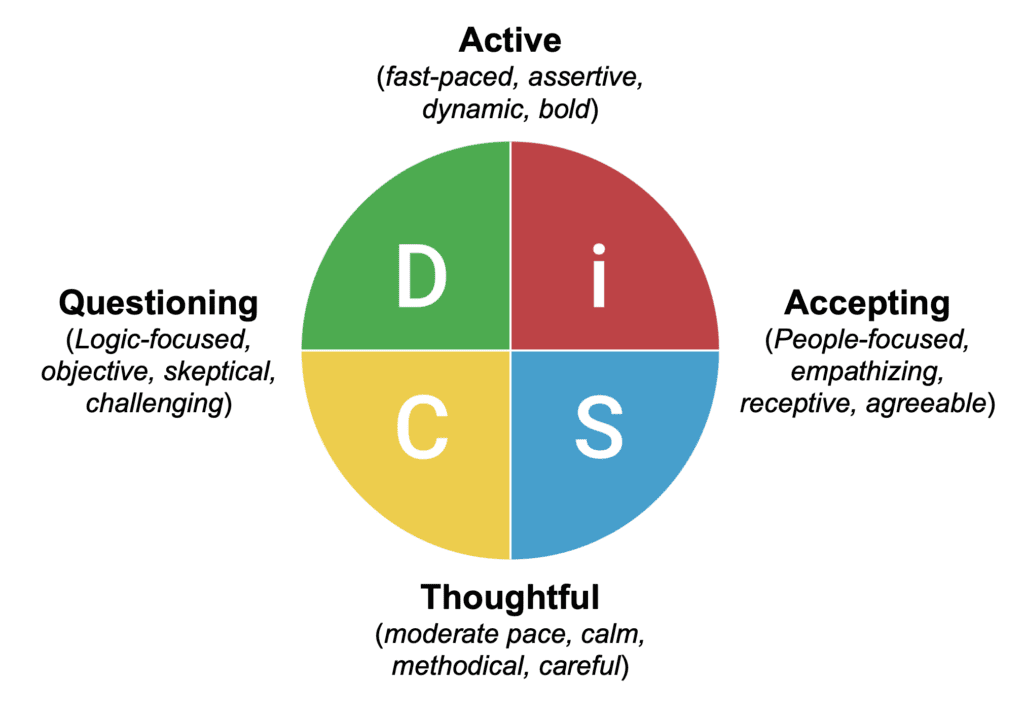
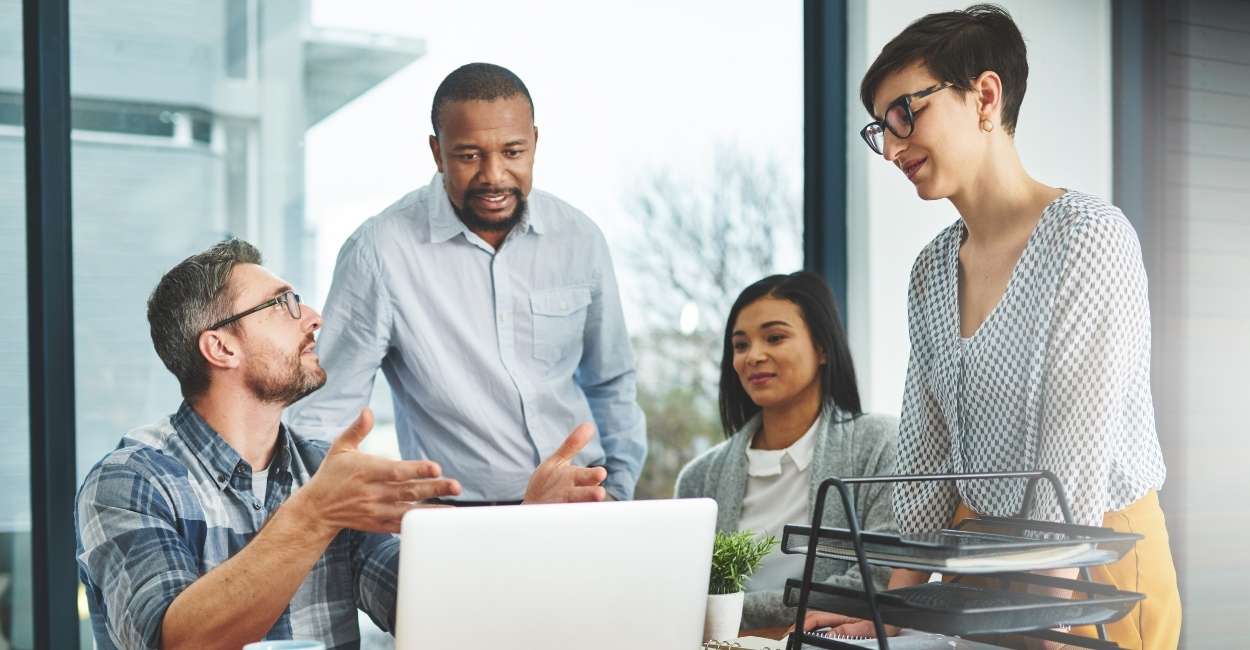
Communicating Effectively
Each of the DISC 4 personality types has a unique style of processing and communicating information. Learning to adjust your approach to theirs increases clarity and engagement.
- With Dominant (D) types, be straightforward, fast-paced, and outcome-oriented. You should avoid small conversations and instead convey the bottom line.
- With Influence (i) types, be kind and cheerful. It’s better to create space for storytelling and open dialogue.
- With Steadiness (S) personalities, communicate with patience and honesty. For this type, consider slow time to reflect and answer.
- With Compliance (C) types, stick to the facts and structure. For effective communication, be thorough and avoid using emotional language.
Navigating Conflict
Miscommunication is frequently the root of conflict, and the DISC model communication styles can have a significant impact.

- D vs. S personalities may conflict because one goes quickly and the other takes time to process.
- I vs. C types may irritate one another if one is systematic and the other is impulsive.
The DISC framework can help you predict these differences and handle sensitive talks with awareness. For example, if you're discussing a problem with a high-S colleague, avoid using combative language and instead express your worries with empathy and certainty.
Building Stronger Relationships
DISC is fundamentally a technique for fostering relationships. Regardless of who you are, aligning your communication style with others promotes trust and psychological stability.
- Managers can motivate staff by providing feedback in a manner that suits their personality.
- Teams can work together more effectively by being aware of one another's preferences.
- Remote workers can personalize emails and video conversations based on their colleagues' DISC type.
How to Identify DISC Communication Styles in 3 Ways
Understanding DISC communication styles is most useful when you can identify them in real time, whether you're interacting with a coworker, client, or manager. While formal assessments provide clarity, many people can recognize styles by observing patterns in behavior, speech, and decision-making.
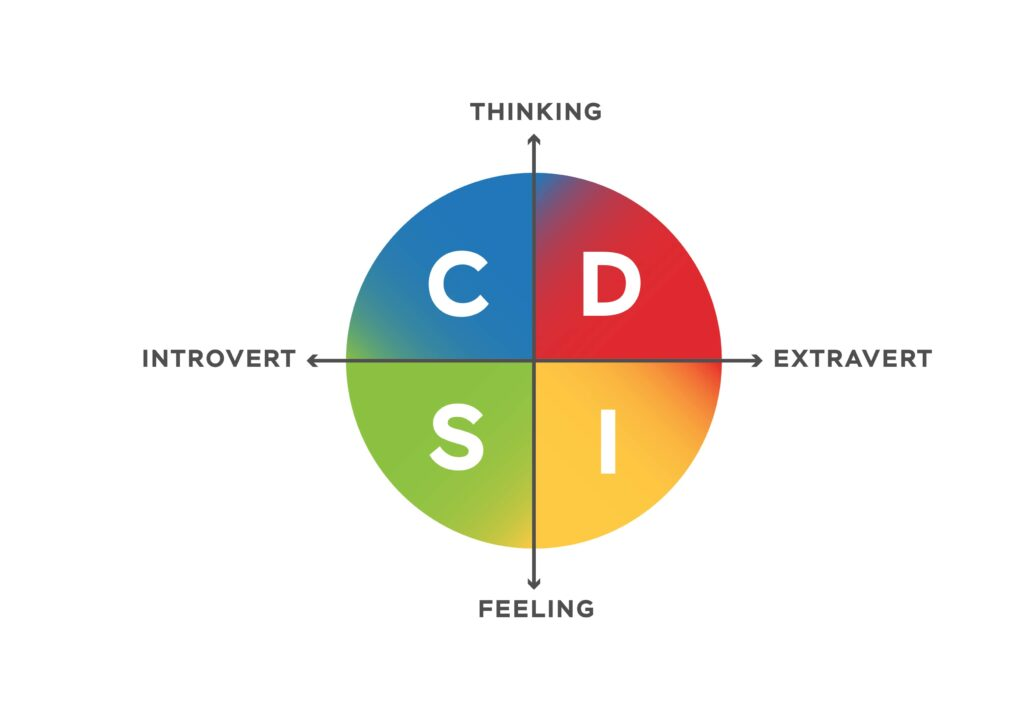
1. Observe Communication Patterns
Each DISC type tends to communicate predictably. Noticing how someone speaks, listens, and responds can offer strong clues about their dominant style:
- D types are fast-paced, direct, and focused on results. They speak with urgency and are usually assertive in meetings.
- i types are expressive, enthusiastic, and animated. They often use stories, humor, or emotional appeals.
- S types are calm, patient, and loyal. They ask questions to ensure harmony and may avoid conflict.
- C types are reserved, analytical, and thorough. They prefer written communication and like to process information before responding.
2. Ask Reflective Questions
If you're unsure of someone's style, consider how they might answer these questions:
- Do they focus more on tasks or people?
- Are they more fast-paced or steady?
- Do they prefer big-picture thinking or detailed analysis?
Even these simple distinctions can help narrow down whether someone is more of a D, i, S, or C—or possibly a blended style.
3. Use Assessments for Accuracy
While it's helpful to observe communication habits, using a formal DISC assessment is the most reliable way to identify someone's style with accuracy. These tools are designed to measure behavioral tendencies based on the DISC model communication styles. They provide clear, personalized profiles that highlight a person’s natural strengths, challenges, and preferences.
Many teams start with a DISC communication styles free test to open up the conversation. Tests remove the guesswork and allow for meaningful team development, leadership training, and personal growth. Knowing someone’s style makes it easier to apply the right communication strategies in meetings, feedback sessions, or conflict resolution.
For a deeper insight, consider taking some Free Personality Test.
Final Thoughts
Understanding DISC communication styles is more than just knowing a theory; it's about strengthening relationships with those around you. Recognizing and respecting different communication styles can help to improve the effectiveness of any encounter. The DISC model's communication styles are attractive because they are simple and adaptable. This framework helps you reduce misconceptions by guiding you through the core DISC 4 personality types and the more complex 12 style blends. Furthermore, it settles conflicts with confidence and fosters more inclusive, collaborative cultures.
FAQs
What is the most common DISC communication style?
While it varies by population, studies often show that Steadiness (S) is the most common among the DISC 4 personality types. S-types are known for their patience, reliability, and preference for supportive, steady communication.
Can you be a combination of two DISC styles?
Yes. In fact, most people are a blend of two styles - such as Di (Dominance + Influence) or SC (Steadiness + Compliance). These blended styles help explain the more subtle differences in behavior, making the DISC model more adaptable to real-world personalities.
How can DISC help in a team setting?
DISC communication styles are especially useful in teams because they help members understand each other’s preferences. This leads to clearer communication, fewer misunderstandings, more effective collaboration, and a more respectful, productive work culture.
Can DISC styles change over time?
Your core style tends to remain stable, but how you express it can evolve depending on your environment, role, or life experience. For example, someone who once preferred a reserved style may become more assertive in leadership roles. Assessments can help track these changes.
Is DISC only for workplace use?
No. While DISC is popular in professional settings, its value extends far beyond the office. DISC communication styles can improve relationships in personal life, education, coaching, customer service, and more. Anywhere people interact, DISC can enhance understanding and connection.


Don't Let Your Potential Stay Hidden!
Take the DISC test today and discover your unique 'YOU', with deep insights into your true personality and potential.
Represents your instinctive behaviors and desires.
Shows the behavioral tendencies you think you should exhibit in specific situations.
Related articles
You may also be interested in
 DISCJan 06, 2026
DISCJan 06, 2026DISC Personality Test for Sales: Unlock Your Team’s Full Potential
DISC Personality Test for Sales helps sales teams improve role fit and performance. Learn how DISC boosts hiring, coaching, and customer alignment.
 DISCJan 06, 2026
DISCJan 06, 2026How to Read DISC Test Results: Understanding Your Personality Profile
Learn how to read DISC test results and understand your personality profile. Discover how DISC can enhance communication, teamwork, and career growth.
 DISCDec 31, 2025
DISCDec 31, 2025What Is Group Culture? How Team Behaviors Shape Workplace Success
Discover what is group culture and how it shapes team dynamics, decision-making, and performance. Learn how the DISC model can help improve your team’s culture.
